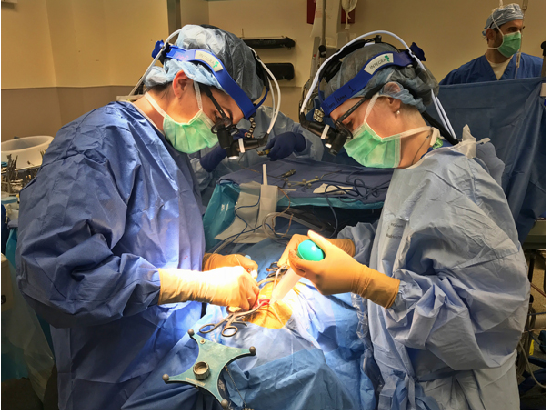
Neurosurgery in Iran
It is a kind of surgery focusing on brain and spinal cord and everything related to sensory and motor nerve. You can easily trust our professional and experienced doctors and surgical team for your neurology problems .
Why do we recommend Neurosurgery in Iran?
Neurosurgery is a very common procedure in Iran. If you are looking for a safe and affordable neurosurgery outside of your country, consider adding Iran to your list of options due to the following three reasons:
Modern doctors who excel and hospitals: The surgical treatment of brain problem in Iran with surgical team who have high scientific and practical experience in conducting medical methods and techniques. Iran – especially in major cities – also enjoys having modern medical facilities that are proud of providing the best medical standards, and these hospitals use advanced equipment and highly professional medical staff work in order to provide the best health care services – including various types of brain surgeries – to patients. Iranians and foreigners.
Attractive prices : Neurosurgery in Iran offers attractive prices compared to other countries. For more information, check the cost of neurosurgery in Iran.
The absence of waiting lists : because you are a person traveling to another country on a medical tourism trip, you will not want to remain on a waiting list for a neurologic operation in Iran, and if you want to perform the operation through a medical tourism institution, it will organize the operation and travel dates so that you do it In just a few days . Make sure to choose a medical tourism establishment that is well known and has a good reputation for providing services to foreign patients.
What is neurosurgery?
Neurosurgery is a specialized branch of surgery that focuses on the diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation of disorders that affect any part of the nervous system, including the brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves, and the vascular system of the brain. This field includes a wide range of procedures from minimally invasive surgeries to complex operations on the brain and spinal cord. Highly trained medical professionals, neurosurgeons use advanced technology and techniques to perform delicate surgeries that significantly improve a patient’s quality of life.
1.What conditions do neurosurgeons treat?
Neurosurgeons treat a variety of conditions such as brain tumors, spinal cord injuries, herniated discs, chronic pain, epilepsy, aneurysms, and congenital anomalies. They also manage conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and other neurological disorders.
2. What are the common methods of neurosurgery?
Common neurosurgery procedures include craniotomy, where part of the skull is removed to access the brain. Spinal fusion involves joining two or more vertebrae to eliminate movement and provide stability. Laminectomy is the removal of a portion of the vertebral bone called the lamina. Stereotactic surgery is a minimally invasive procedure that precisely targets specific areas within the brain .
3. What is minimally invasive neurosurgery?
Minimally invasive neurosurgery involves techniques that use smaller incisions and advanced tools to perform surgeries with less damage to the body. Benefits include reduced pain, shorter hospital stays, faster recovery times, and reduced risk of complications.
4. What should I expect during recovery after neurosurgery?
Recovery after neurosurgery varies depending on the type and complexity of the operation. Patients may experience pain and discomfort that can be controlled with medication. Physical therapy and rehabilitation are often necessary to regain strength and function. Follow-up appointments with the neurosurgeon are important to monitor improvement and progress.
5. How do I choose the right neurosurgeon?
Choosing the right neurosurgeon involves researching credentials, experience, and patient reviews. It is important to find a board-certified neurosurgeon who specializes in treating your specific condition. Consulting with several surgeons can help you make an informed decision.
The importance of neurosurgery
Neurosurgery plays an important role in the management and treatment of complex neurological diseases that can significantly affect a person’s life. Advances in neurosurgery techniques and technology have made it possible to treat conditions that were once considered inoperable. Early intervention by a skilled neurosurgeon can prevent the progression of neurological diseases and improve overall outcomes. With a focus on patient-centered care, neurosurgeons work closely with other health care professionals to provide comprehensive treatment plans tailored to the patient’s needs.
Illness of neuro :
brain tumors
Brain tumors are abnormal growths of cells in the brain. They can be classified as benign (noncancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Understanding the type of tumor is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment and management strategy. They may originate in the brain (primary tumors) or spread from other parts of the body (secondary or metastatic tumors). Symptoms vary based on the tumor’s size, location, and growth rate. Common symptoms include headaches, seizures, vision or hearing problems, and changes in personality or behavior. Neurosurgery often involves removing as much of the tumor as possible while preserving brain function. Advanced techniques such as stereotactic surgery and intraoperative imaging improve the accuracy and safety of these procedures.
spinal damage
Spinal cord injuries (SCIs) result from damage to the spinal cord that results in loss of function, such as mobility or sensation. These injuries can result from trauma (eg, car accidents, falls) or non-traumatic causes (eg, tumors, infections). The severity of SCI depends on the location and extent of the injury. Symptoms can range from partial loss of movement and sensation to complete paralysis below the injury site. Neurosurgical intervention may include decompression, stabilization, or realignment of the spine to prevent further damage and recovery. Rehabilitation and physical therapy are critical components of treatment to help patients regain independence and improve their quality of life.
herniated disc
A herniated disc occurs when the soft inner gel of the intervertebral disc protrudes through a tear in the harder outer layer. This can compress nearby nerves and cause pain, numbness, or weakness in the limbs. A herniated disc, which usually affects the lumbar (back) spine, can also occur in the cervical (neck) spine. Conservative treatments such as physical therapy, drug therapy, and injections often relieve symptoms. However, when these treatments fail, neurosurgery may be necessary to remove the herniated disc and relieve pressure on the nerve, which can significantly reduce pain and improve function.
epilepsy
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder characterized by frequent, unprovoked seizures due to abnormal electrical activity in the brain. Seizures can vary from brief interruptions in attention to severe seizures and loss of consciousness. While many epilepsy patients manage their condition with medication, some do not respond and may benefit from surgical intervention. Neurosurgeons can perform resective surgery to remove the area of the brain that causes seizures. Additionally, palliative procedures like vagus nerve stimulation or responsive nerve stimulation can help reduce the frequency and severity of seizures.
Aneurysm
Aneurysms are weak, bulging areas in the walls of blood vessels, often found in the brain’s arteries. If an aneurysm ruptures, it can cause a life-threatening hemorrhagic stroke. Symptoms of an unruptured aneurysm may include headache, vision problems, or neurological deficits. A ruptured aneurysm typically causes a sudden, severe headache, nausea, and loss of consciousness. Neurosurgeons treat aneurysms with clipping, where they place a metal clip at the base of the aneurysm to block blood flow. Another option is endovascular coiling, where they insert coils into the aneurysm to induce clotting and dislodge it Block blood flow.
Parkinson’s disease
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder that affects movement. This occurs due to the loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain, leading to tremors, stiffness, slowness of movement, and balance problems. Medications can help manage these symptoms. However, advanced stages of Parkinson’s disease may require neurosurgical interventions like deep brain stimulation (DBS). In DBS, electrodes are implanted in specific brain areas to regulate abnormal electrical impulses. This procedure can significantly reduce motor symptoms and improve the quality of life for many patients.
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a condition characterized by an abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the ventricles of the brain. This can lead to increased intracranial pressure, causing symptoms such as headaches, nausea, vomiting, balance problems, and cognitive impairment. In infants, it may cause an enlarged head. Hydrocephalus can be congenital or acquired due to infection, tumor, or hemorrhage. Neurosurgical treatment typically involves placing a shunt system to divert excess fluid from the brain to another part of the body where it can be absorbed. Alternatively, an endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV) creates a new path for cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flow.
meningitis
Meningitis is an inflammation of the meninges, the protective membrane that covers the brain and spinal cord, often caused by bacterial, viral, or fungal infections. Symptoms include severe headache, fever, neck stiffness, sensitivity to light, and altered mental status. Bacterial meningitis is particularly severe and requires immediate medical treatment to prevent complications such as brain damage, hearing loss, or death. Neurosurgical intervention may be necessary to remove complications such as brain abscess or reduce pressure caused by swelling. Treatment usually includes antibiotics or antiviral drugs and supportive care in the hospital.
spinal disorders
Spine and spinal cord tumors: These tumors can be benign or malignant and can arise from the spinal cord itself, surrounding membranes or vertebrae. Symptoms include pain, neurological deficits, and sometimes paralysis, depending on the location and size of the tumor. Treatment often involves surgical removal, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy to remove or shrink the tumor and reduce symptoms.
Injuries and fractures of the spinal vertebrae often result from falls, accidents, or sports impacts. If the spinal cord is damaged, it can cause pain, instability, and neurological deficits. Neurosurgical treatment aims to stabilize the spine and decompress the nerves or spinal cord. Surgeons often use techniques like vertebroplasty, spinal fusion, or placing rods and screws to achieve this .
Slipping of the spinal vertebrae (spondylolisthesis): This condition occurs when one of the vertebrae slips on the one below it, causing pain, stiffness and compression of the nerve. Symptoms may include back pain, leg pain, and neurological symptoms. Surgical intervention, such as spinal fusion, is often needed to realign and stabilize the vertebrae, relieve pressure on the nerves, and restore spinal stability.
Spinal canal stenosis: Spinal canal stenosis is the narrowing of the spinal canal that can put pressure on the spinal cord and nerves and lead to pain, numbness and weakness in the limbs. This condition is often caused by degenerative changes such as arthritis. Neurosurgical treatments, including laminectomy or laminotomy, aim to decompress the spinal canal and relieve symptoms.
spinal damage
Cerebral embolism (bubble in the bloodstream): Also known as an air embolism, this happens when air bubbles enter the bloodstream and travel to the brain, blocking blood flow. It can cause stroke-like symptoms such as sudden weakness, confusion, and loss of consciousness. Immediate medical intervention is critical, often including hyperbaric oxygen therapy to reduce the size of the bubbles and restore normal blood flow.
Thrombosis in the brain’s blood vessels can block blood flow to a part of the brain, leading to an ischemic stroke that causes brain cells to die. Symptoms include sudden numbness, difficulty speaking, and loss of coordination. Neurosurgical intervention may include mechanical thrombectomy to physically remove the clot and restore blood flow.
Damage to blood vessels in the brain can result from trauma, aneurysms, or vascular abnormalities. These issues may lead to hemorrhagic strokes or other neurological defects. Treatment depends on the cause. It may include surgical clipping or coiling of aneurysms, repair of vascular malformations, or management of traumatic injuries. Various neurosurgical techniques are used to control bleeding and repair damaged vessels.