Obesity and infertility – What is infertility?

Obesity and infertility
What is infertility?
In general, infertility means the inability to conceive after one year (or more) of unprotected sex.
What are the factors affecting infertility in women?
- Age
- olycystic ovary syndrome
- Hormonal problem that prevents ovulation
- Abnormal menstrual cycle
- Obesity
- Diabetes Thyroid problems
- Alcohol and smoking
- Having a small amount of body fat due to intense exercise.
- Endometriosis Structural problems (problems with the fallopian tubes, uterus, or ovaries)
- Infection
- And other items
What are the factors affecting male infertility?
- Age
- Smoking and alcohol consumption
- Obesity
- Varicocele
- Diabetes Thyroid problems
-
- Infection
- Ejaculation issues Antibodies that attack sperm
- Tumors
- Dropped testicles
- Hormonal imbalance Defects in sperm transfer tubes
- And other items
There is a strong link between obesity and infertility, and weight loss can increase fertility in obese women.
Obesity has reduced fertility in both men and women.
What is the relationship between obesity and infertility?
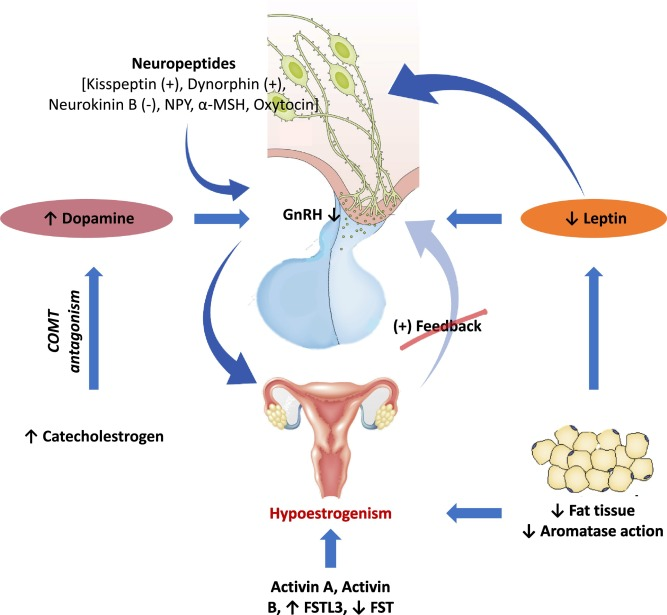
Overweight and obese people have higher levels of a hormone called leptin, which is produced in adipose tissue. This can upset the hormonal balance and lead to reduced fertility.
The amount and distribution of body fat affects the menstrual cycle through a wide range of hormonal mechanisms. The more excess weight and belly fat, the greater the risk of fertility problems. Overweight, especially excess belly fat, is related with resisting to insulin (when the body needs to produce more insulin to maintain normal blood sugar levels) and lowering sex hormone-binding globulin (SHGB), a protein that regulates androgens and Estrogen.
This increases the risk of irregular menstrual cycles, which in turn reduces fertility. One study found that obese women were much less likely to become pregnant within a year of stopping contraception than women in the normal weight range (66.4% of obese women became pregnant within 12 months). , While 81.4% of women with normal weight got pregnant within this time).
The hormonal balance that regulates the menstrual cycle is altered by overweight and obesity and also increases the risk of not ovulating (when the egg is not released by the ovary). Women with a body mass index (BMI) above 27 are three times more likely to not become pregnant than women in the normal weight range because they do not ovulate.
Many overweight women are still ovulating, but the quality of the eggs they produce seems to be declining.
And when couples use IVF to get pregnant, women who are overweight or obese are less likely to give birth alive and normal infants than women with a normal BMI. On average, compared with women in the healthy weight range, the probability of live and healthy birth with IVF is 9% lower in overweight women and 20% lower in obese women.
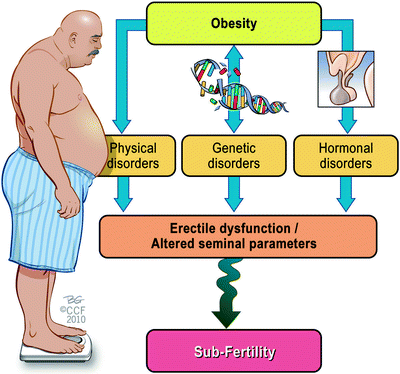
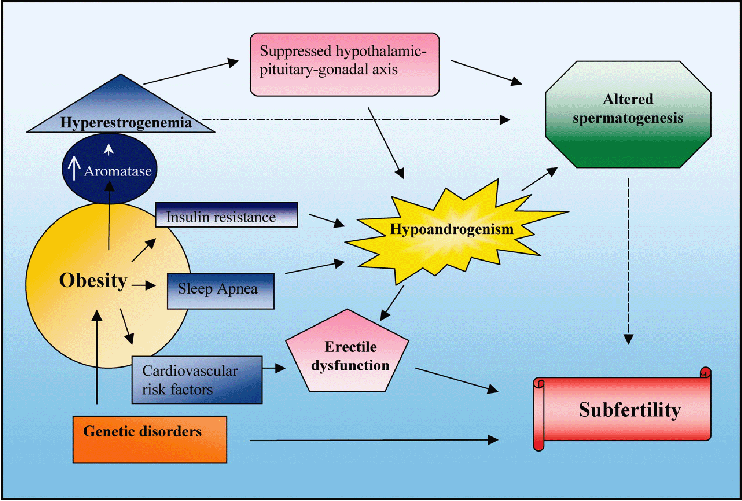
In men, obesity is also associated with reduced fertility. This is most likely due to a combination of factors. These include hormonal problems, sexual dysfunction and other obesity-related health conditions such as type 2 diabetes and sleep apnea (both of which are associated with low testosterone levels and erectile problems).
It is estimated that weighing more than 10 kg reduces male fertility by up to 10%. Studies of the effects of obesity have shown that obese men are more likely to be infertile and less likely to have a live and healthy birth if they use assisted reproductive technology (ART) such as IVF.
This is thought to be because obesity not only reduces sperm quality, but also alters the physical and molecular structure of sperm cells.
The effect of bariatric surgery on male fertility
1.Sex hormones were the most common results evaluated, showing significant improvement in all studies with male patients. In general, weight loss after bariatric surgery led to an increase in total and free testosterone levels and a decrease in estradiol levels.
- Sex hormones: Significant improvement has been reported for all findings (sex hormones and sex hormone globulin) and it has also been found that testosterone improvement is affected by age.Men under 35 years of age showed a greater postoperative increase in free and total testosterone than men over 35 years of age. Three studies compared obesity surgery with the control or non-surgical group and showed greater hormonal improvements in the obesity surgery group than in the control group.
- 2.Seminal output (semen): Among the four studies that examined the quality of semen or sperm, two studies reported improvements in baseline parameters.Viability and volume of the sperm after surgery improved significantly compared with the control group (non-surgical group) in one study, and the number of sperms in the subgroup analysis improved significantly and showed that patientswith azoospermia or oligospermia have significantly increased sperm counts, while patients with normal sperm counts from the beginning showed no postoperative difference.
3.Sexual performance and satisfaction: A study (2009) reported a positive relationship between obesity surgery and patients’ sexual quality of life. Another study (2015) showed no significant improvement in male erectile function, but showed a recovery process 12 months after surgery. In another study (2012), the International Erectile Performance Index (IIEF-5) questionnaire was used and reported a significant mean score at 24 months postoperatively in the surgical group and also a significant difference compared to the control group.
The effect of bariatric surgery on female fertility
- 1.Sex hormones: In three studies, measurements of various fertility hormones, a significant decrease in testosterone and an increase in SHBG in postoperative women were reported.The most significant changes in SHBG occurred within one month after bariatric surgery and continued for up to 12 months. Two studies also reported a significant increase in estradiol. Other hormones, including FSH and LH, showed no significant postoperative changes.Two studies have also reported that hirsutism in women resolves due to improved hormonal balance after surgery.
- 2.Menstrual periods: Six of the eight menstrual cycle measurement studies in obese patients reported a significant improvement in menstrual cycle order and length.For example, the menstrual cycle at 12 months after RYBG (classical bypass) in 85% of women with oligo-amenorrhea was improved, and the rate of irregular menstruation was decreased from 60% to 20% after sleeve surgery and the rate of menstrual dysfunction after differentObesity surgeries decreased by 12.4%.
(Oligomenorrhea = infrequent menstruation that has intervals of more than 35 days and amenorrhea = no menstrual bleeding in women of childbearing age)
- 3.Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Two studies measuring PCOS reported significant improvement over 3 to 12 months. In particular, in a 2017 study, PCOS was defined based on the Rotterdam criteria. Before surgery, 25% or 8 of 31 patients had polycystic ovary syndrome. After three months, only one in eight patients still met the PCOS criteria, and after 12 months, none were classified as PCOS. In another study. (2016), PCOS were evaluated based on the number of patients with PCOS before and after obesity surgery. Diagnosis of polycystic ovary syndrome was performed in 1298 patients before surgery and 1,106 patients after surgery, which showed a decrease of 14.8%.
- 4.Pregnancy: In a 2012 study, 100% fertility was reported in patients previously infertile due to polycystic ovary syndrome.Four other studies reported an improvement in pregnancy rates after obesity surgery.Seven of the 15 women who failed to conceive became pregnant after gastric sleeve surgery (46.7%), and 62.7% of patients who could not conceive became pregnant after various surgeries, including gastric sleeve and gastric bypass surgery.
- 5.Sexual performance and satisfaction: In a study that examined sexual function, satisfaction, or intimacy, it was shown that using the Female Sexual Performance Index Scale at 12-month follow-up, there was a significant improvement in female sexual function.
The results of these studies show that fertility improves after obesity surgery for obese male and female patients.
What happens if you get pregnant too soon after obesity surgery?
What we are concerned about is vitamin deficiency in mothers as well as neural tube defects in infants. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists warns that increased fertility after bariatric surgery can lead to unplanned pregnancies. Delaying it allows the woman to reach a constant weight during fetal development.
How long do I have to wait to get pregnant after obesity surgery?
How long do you have to wait after the operation to get pregnant? Experts suggest that a woman should wait 1 to 2 years after obesity surgery to become pregnant. This surgery helps people to lose a lot of weight quickly. Getting pregnant too soon after surgery may mean that the growing baby may not be getting the nutrients he or she needs.
In addition to the positive effects mentioned for weight loss in improving fertility, due to the impact of factors such as diabetes, thyroid problems and other factors mentioned above in male and female infertility, weight loss surgeries can also improve these factors and problems that could be effective in improving fertility.